Products
- Home
- Products
- Product/technological information
- Basic Rules for Selecting and Handling Bearings
Product/technological information
13. Basic Rules for Selecting and Handling Bearings
Selection of Bearings
(1) The performance of a thin-section bearing heavily relies on the accuracy of the shaft and housing. The accuracy around the bearing must fully meet the conditions indicated in the fittings chart. Particularly, if you have any questions regarding the use of 6700 and 6800 series products, feel free to consult with us.
(2) If you are planning to use a bearing with a snap-type (W) cage for high-acceleration, heavy-load, and impact-load applications, for the vertical shaft, and/or with force-feed oil lubrication, and if you have any questions, feel free to consult with us.
(3) You must select the fitting, clearance, lubrication method, and lubricant carefully by fully taking into account the rotational speed, load, and temperature, in order to prevent anomalies such as seizure, premature flaking, and large noise from taking place.
(4) Full complement ball bearings are suited for low-speed and heavy-radial-load applications. You must fully comply with the usage conditions because the balls may fall out of the slot groove with a relatively small axial load.
Handling and Storage of Bearings
(1) In order to prevent the formation of rust, bearings should be stored in an environment at a temperature of around 20°C and a humidity of 65% or less. Do not place them directly on the floor (it is desirable to store the bearings on a shelf at least 30 cm above floor), avoid direct sunlight and contact with cold wall surfaces.
(2) The bearings should be handled in a clean environment, making sure any sweat or dirt from your hands do not get attached. Also, bearings should be handled by those with extensive knowledge on bearings, based on the defined work standard. Above all, the bearings must be handled carefully to avoid any damage, indentation, and chipping.
(3) Placing the bearings in an acidic atmosphere may result in rust and discoloration. Also, if you use cotton work gloves or waste cloth to wipe the bearing, shaft, or housing, dust may enter the bearing or the fitting, which may cause anomalies. Make sure to avoid these situations.
Mounting
(1) Precautions before mounting
a) The bearing should be mounted in a clean environment, using clean mounting jigs and tools.
b) When mounting a new bearing, do not open its package until immediately before the mounting process.
c) Make sure to seal the container of the oil or grease to be used.
d) Wash the shaft and housing, and check in advance that they are free of any damage, indentation, and deformation.
e) When using grease lubrication, use the bearing directly without washing it.
f) When using an open bearing, wash off the corrosion inhibiting oil and apply an appropriate lubricant before use.
Feel free to consult with us if you wish to have the product filled with a lubricant before shipping.
(2) Shaft and housing inspection
a) Check whether the dimensions, accuracy, and finish surface roughness of the shaft and housing are in accordance with the designated specifications. If the fitting surface is too rough, the fitting may loosen during use, which may cause creep. If the roundness of the corners is larger than the bearing chamfer rsmin, or the shoulder surface is inconsistent, the bearing cannot be mounted perpendicularly, which will cause a large moment load and deviated rotation, resulting in a shorter life.
b) The shaft length changes depending on the temperature; therefore, when two or more bearings are mounted on a shaft for use, the normal practice is to fix one bearing and allow another bearing to move within the housing. If this is the case, you must check that the clearance in the axial direction allows this bearing to move.
How to Mount a Bearing
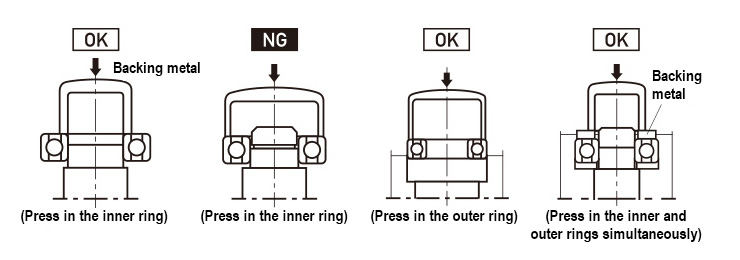
(1) Inner ring interference fit
A press machine should be used to press in small bearings with inner ring rotating load and small interference. When a large interference and/or a large bearing are used, shrink fit should be performed at a temperature of 120℃ or less either in oil or by using an induction-heating device, etc.
(2) Outer ring interference fit
A press machine should be used to press in small bearings with outer ring rotating load and small interference. When a large interference and/or a large bearing are used, cooling fit should be performed, using dry ice and the like. In this case, you must consider introducing waterproofing measures to prevent rusting.
(3) Outer and inner rings’ interference fit
When the outer and inner rings must be pressed in at the same time, a backing metal should be used to enable simultaneous contact of the inner/outer rings’ faces. Before the press-in process, you may want to apply high-precision oil onto the fitting surfaces of the shaft and housing.
Operation Check
(1) Small devices should be rotated manually to check that they are free of any excessive torque, uneven rotation, and snags.
(2) Devices that cannot be rotated manually should be started with no load and immediately switched to coasting, then you should perform the checks as with (1) above.
(3) If no anomalies are found in (1) or (2) above, conduct a powered trial run where the power is increased slowly from no load and low speed to standard rotation. Here, you should check that there are no anomalies in terms of temperature rise and vibrations.
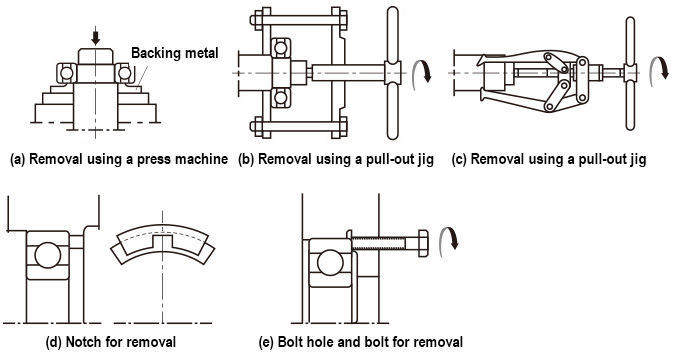
How to Remove a Bearing
(1) In case you may need to remove the interference fit bearing in the future with an aim to reuse it or investigate the cause of a defect, you should design and create a dedicated jig so that you will be able to remove the bearing easily without causing any damage.
(2) When using a press machine to remove the inner ring of the interference fit, you should place a backing metal against the inner ring. In addition, if a shaft design that can be grappled is employed, you may be able to use a puller to remove the bearing.
(3) For removal of the outer ring of the interference fit, it is recommended to create a bolt screw hole or a notch at the shoulder of the housing.